DDA / Accessibility
The Disability Discrimination Act seeks ‘to eliminate, as far as possible, discrimination against persons on the ground of disability”. Within public spaces and transport infrastructure, the objective is to enable access for everyone.
Some of the visible changes resulting from the DDA legislation include:
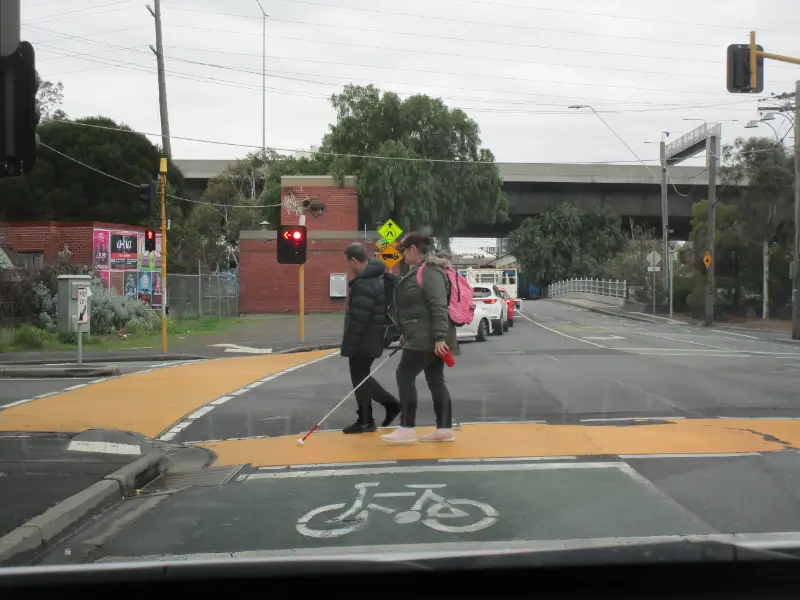
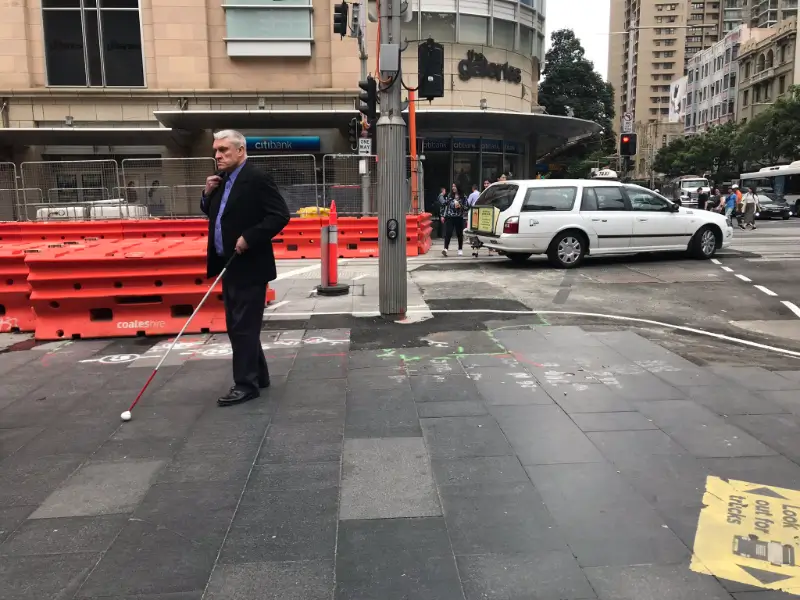
- Tactile Ground Surface Indicators (TGSIs) to assist people with vision impairments of the direction of paths and crossings and to warn them of hazards;
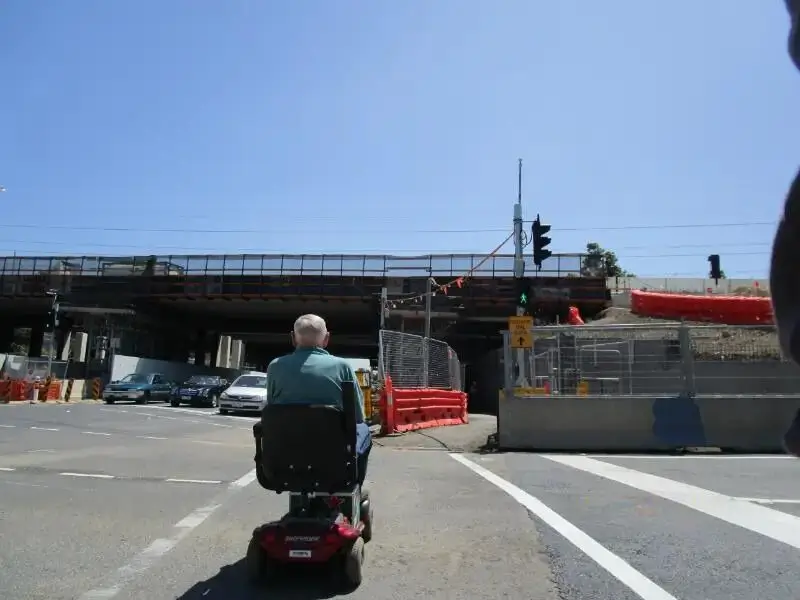
- Ramps, landings and handrails to assist people with mobility impairments;
- Public transport stops that are accessible for people with mobility impairments.



DDA and accessibility is also supported by other laws and regulations. In particular, public transport operators have obligations within the Disability Standards for Public Transport (DSAPT) Act 2002. The Act and related regulations are intended to provide universal access to public transport services and facilities allowing all passengers independent travel.
RSA has established itself as a leader in DDA and DSAPT accessibility and safety audits. Our team has experience undertaking accessibility audits in many settings within public open spaces, public transport environments and the built-environment. Our team is experienced in undertaking pragmatic assessments to ensure practical accessibility can be achieved within existing infrastructure redevelopments, new developments, urban design and public transport.
The Disability Discrimination Act, 1992 (DDA), the Disability Standards for Access to Public Transport 2002 (DSAPT) and the Disability (Access to Premises, Buildings) Standards 2010, (DAPS), within public spaces, buildings and transport infrastructure
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of the DDA, DAPS and DSAPT and their pivotal role in enhancing accessibility within public spaces and transport infrastructure. In a world that thrives on diversity and inclusivity, understanding these legislations’ impact is crucial. These legislation support individuals with disabilities, championing equal opportunities and access across various facets of life.
From installing ramps and adapting facilities to ensuring digital platforms are user-friendly for all, the DDA, DAPS and DSAPT are reshaping our environment to be more inclusive. Our discussion will delve into why accessibility is indispensable, the significant changes it has brought about, and how organisations can align with required standards to foster a welcoming atmosphere for everyone. Join us as we navigate through the essentials of these legislative instruments, their benefits for businesses, and the importance of comprehensive accessibility and safety audits.
This journey is not just about adhering to legal requirements; it’s about building a society that values every individual’s right to access and participate fully in public life.
What is DDA, DAPS and DSAPT and how do they impact accessibility?
The DDA and associated legislation including the Disability Standards for Access to Public Transport 2002 (DSAPT) and the Disability (Access to Premises, Buildings) Standards 2010, (DAPS) are crucial legislation designed to eliminate discrimination against people with disabilities. Their foremost objective is to ensure that individuals with disabilities enjoy equal opportunities in various aspects of life, such as employment, education, and access to goods and services. Theses acts significantly impacts accessibility by requiring both public and private sectors to make reasonable adjustments to accommodate the needs of people with disabilities, thereby fostering inclusivity and accessibility.
Under the DDA, DSAPT and DAPS, organisations are compelled to implement changes to their physical environments or the manner in which services are delivered to ensure they are accessible to people with disabilities. This encompasses actions like installing ramps, adapting restrooms, or providing information in accessible formats.
The influence of these legislative instruments goes beyond mere physical and digital modifications; it cultivates a culture of awareness and inclusivity. It encourages society to acknowledge and tackle the obstacles faced by people with disabilities. Consequently, these legislation only aids individuals with disabilities but also enhances the community at large, advocating for diversity and equality.
In essence, these legislative instruments stand as a fundamental forces in combating discrimination, ensuring that people with disabilities have equal access and opportunities. Its impact on accessibility is significant, mandating concrete changes to environments and services, and promoting an inclusive society where everyone can participate fully and equally.
Why is accessibility important?
Accessibility is crucial because it ensures equal access for people with disabilities, thereby promoting inclusivity in public spaces. It mandates adjustments in both public and private sectors, effectively removing barriers that might otherwise prevent individuals with disabilities from fully participating in society. This not only enhances the quality of life for people with disabilities but also enriches the community by fostering a diverse and inclusive environment.
Ensures equal access for people with disabilities
Accessibility mandates modifications in environments and services, ensuring people with disabilities have the same opportunities to access public spaces, employment, education, and digital platforms. This equal access is fundamental to fostering independence and self-reliance among individuals with disabilities, aligning with principles of fairness and equality.
Promotes inclusivity in public spaces
By requiring adjustments that accommodate the needs of people with disabilities, accessibility champions the creation of inclusive public spaces. This inclusivity not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also enhances the social fabric by encouraging a culture of diversity and acceptance.
What are some of the key changes of accessibility legislation?
The legislation requires changes aimed at enhancing accessibility for people with disabilities. These changes include:
- Tactile Ground Surface Indicators (TGSIs): These features assist individuals with vision impairments by indicating the direction of paths and crossings and warning of potential hazards.
- Ramps, landings, and handrails: Essential for people with mobility impairments, these modifications facilitate smoother and safer access to various environments.
- Accessible public transport stops: Ensuring that individuals with mobility impairments can access public transport stops is crucial for promoting independent travel and access to essential services.
Tactile Ground Surface Indicators (TGSIs) to assist people with vision impairments
TGSIs are designed to aid individuals with vision impairments by providing tactile feedback on the direction of paths and crossings, and alerting users to potential hazards. This feature plays a pivotal role in ensuring safer navigation through public spaces, thereby enhancing autonomy and security for visually impaired persons.
Ramps, landings, and handrails to assist people with mobility impairments
The incorporation of ramps, landings, and handrails are crucial for continuous paths of travel (CAPT) for people with mobility impairments. These adjustments enable easier and safer movement into and within public areas and buildings, promoting independence and inclusivity for individuals who rely on these features for mobility.
Public transport stops that are accessible for people with mobility impairments
Making public transport stops accessible to individuals with mobility impairments significantly advances the inclusivity of the public transport system. This accessibility empowers persons with mobility challenges to travel more freely, supporting their right to mobility and access to the community and essential services.
How can we help organisations comply with DDA, DAPS and DSAPT accessibility obligations?
To assist organisations in achieving compliance with DDA, DAPS, DSAPT and other federal and state standards and codes,, our approach encompasses several key steps:
- Conducting accessibility audits: We meticulously assess the current state of facilities and services to identify any barriers that hinder accessibility, ensuring a thorough understanding of areas that fall short of requirements.
- Identifying barriers to access: Our analysis pinpoints specific obstacles within an organisation’s environment, providing a clear roadmap of areas needing improvement.
- Recommending necessary modifications: Based on the audit findings, we advise on targeted modifications to enhance accessibility, aligning with DDA standards to foster an inclusive environment.
Our team’s expertise in conducting pragmatic assessments across various settings, including public spaces, transport environments, and the built environment, ensures that practical and effective accessibility solutions are identified and implemented. Through these strategic measures, we guide organisations toward full compliance with legislative requirements, enhancing inclusivity and ensuring equal access for all individuals.
DDA and accessibility is also supported by other laws and regulations
It’s critical to recognise that DDA compliance is part of a wider legal ecosystem, with additional laws and regulations supporting the overarching goal of enhanced accessibility.
Public transport operators have obligations within the Disability Standards for Public Transport (DSAPT) Act 2002
We assist public transport operators in understanding and fulfilling their obligations under the DSAPT Act 2002, which demands universal access to public transport services.
The Act and related regulations are intended to provide universal access to public transport services and facilities allowing all passengers independent travel
Our objective is to ensure the full implementation of the Act’s provisions, promoting universal access and enabling independent travel for all passengers, thereby advancing inclusivity and accessibility across public transport.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with accessibility obligations?
Non-compliance with accessibility obligations can lead to significant consequences for organisations. These include legal penalties, such as fines and legal actions, which arise from failing to meet mandated accessibility requirements. Beyond the immediate legal implications, there are substantial reputational risks.
Negative public perception can greatly impact an organisation’s brand image, leading to a loss of customer loyalty and potentially affecting the bottom line. In essence, failing to adhere to DDA Accessibility standards not only violates legal obligations but also risks alienating a significant portion of the population, undermining principles of inclusivity and equal access.
How does accessibility benefit businesses?
Accessibility benefits businesses by expanding their customer base to include individuals with disabilities, who represent a significant market segment. By fostering a welcoming environment for all customers, businesses not only comply with legal standards but also enhance their reputation as inclusive and socially responsible entities. This commitment to accessibility enhances brand reputation and is viewed positively by consumers, potentially leading to increased customer loyalty.
In essence, aligning with DDA Accessibility standards not only fulfills legal obligations but also serves as a strategic advantage, promoting a positive public image and contributing to the long-term success of a business.
RSA has established itself as a leader in DDA, DAPS and DSAPT accessibility and safety audits
RSA has carved a niche for itself as a frontrunner in conducting comprehensive DDA and DSAPT accessibility and safety audits. With a seasoned team experienced in a wide array of settings, including public open spaces, public transport environments, and the built environment, RSA excels in identifying and assessing accessibility challenges. The organisation’s approach is characterised by pragmatic assessments aimed at ensuring practical accessibility solutions that comply with current regulations and standards.
This expertise not only aids in making environments more inclusive but also supports organisations in meeting their legal obligations under DDA and DSAPT acts, thereby fostering universal access and enhancing safety for all users. RSA’s commitment to excellence and its comprehensive audit services have solidified its reputation as a trusted leader in the field of accessibility and safety audits.
Our team has experience undertaking accessibility audits in many settings within public open spaces, public transport environments, and the built environment
Our team boasts extensive experience in conducting accessibility audits across a diverse range of settings, including public open spaces, public transport environments, and various aspects of the built environment. This breadth of experience ensures a comprehensive understanding of accessibility challenges and solutions in different contexts.
Our team is experienced in undertaking pragmatic assessments to ensure practical accessibility can be achieved within existing infrastructure redevelopments, new developments, urban design, and public transport
Leveraging our expertise, we specialise in performing pragmatic assessments aimed at achieving practical accessibility solutions. Our approach is tailored to enhance accessibility in both existing infrastructure redevelopments and new developments, encompassing aspects of urban design and public transport, ensuring that accessibility considerations are integrated seamlessly into projects from the outset.
Related Case Studies
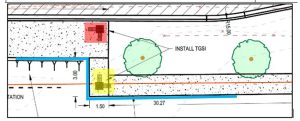
Plenty Road, Doreen, Melbourne
This audit highlighted a common issue with TGSIs within design, namely, overuse.

Waverley Gardens Shopping Centre, Mulgrave, Melbourne
This was a DDA compliance audit for this medium sized suburban shopping centre, covering internals and externals.